Cross-buffer access
EVL drivers can access the out-of-band endpoint of a cross-buffer, to exchange data with a user application which attends the in-band endpoint. The companion driver of the latmus application illustrates this, by transmitting the latency data it measures in kernel space to the display front-end which runs in user space, via a shared cross-buffer.
A driver can achieve this as follows:
-
given a file descriptor to the cross-buffer element created by an EVL application, the driver obtains a stable reference to the
struct evl_xbufdescriptor associated to that cross-buffer in kernel space, by a call to evl_get_xbuf(). This in-kernel descriptor is used for other operations on the cross-buffer. -
from that point, the driver may send/receive data to/from the application via the cross-buffer using the evl_write_xbuf() and evl_read_xbuf() respectively.
-
when the cross-buffer is not needed anymore, the driver should release the reference it has obtained, by calling evl_put_xbuf().
Cross-buffer services
Retrieve a cross-buffer from a file descriptor. Typically, the peer application would pass the file descriptor to the driver using a dedicated ioctl(2) system call in order to establish the communication. The file descriptor is resolved in the context of the caller, i.e. by a lookup into the file table of the current process.
A file descriptor which should point at a cross-buffer element available from user space in the context of the calling process.
A pointer to an EVL file descriptor, referring to the cross-buffer internally. A reference is held on this file, to guarantee it never goes stale until dropped by a converse call to evl_put_xbuf().
evl_get_xbuf() returns the in-kernel
struct evl_xbuf descriptor of the cross-buffer on success, otherwise NULL
if efd is either an invalid descriptor, or does not correspond to a
cross-buffer element.
Release a cross-buffer previously obtained by a call to evl_get_xbuf(). The reference to the corresponding element is dropped.
A pointer to the EVL file descriptor received from evl_get_xbuf() for the cross-buffer to be released.
Attempt to read up to count bytes from the cross-buffer xbuf into
the buffer starting at buf from the out-of-band execution stage. The
data is received from a peer application in user space which sent it
by calling the
write(2) system
call to the same file referred to by the descriptor passed to
evl_get_xbuf().
If O_NONBLOCK is
clear in f_flags, there are no short reads: the caller always gets a
complete message of the requested length, blocking if necessary
except if a sender is currently blocked on the other end of the
channel, waiting for some space to be available into the ring buffer
to complete a write operation. In this case, a short read is performed
to prevent a deadlock, which means the caller may receive fewer data
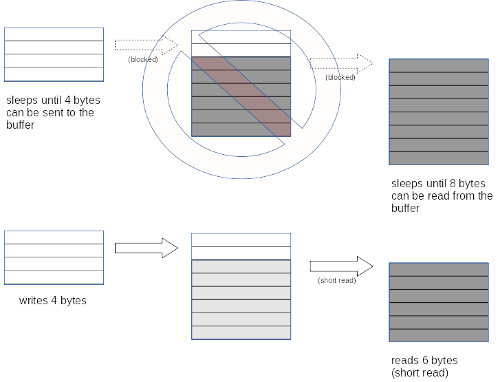
than requested in the evl_read_xbuf() call. This situation arises when the size picked for the ring
buffer does not fit the transfer pattern, as illustrated below:
A cross-buffer descriptor to read from.
A buffer to read the cross-buffer data into.
The number of bytes to read into buf.
Operation flags. Can be either zero or O_NONBLOCK for non-blocking input.
The number of bytes copied to buf is returned on success, otherwise:
-
-EAGAIN if
O_NONBLOCKis set inf_flagsnot enough data is available from the cross-buffer to satisfy the request. -
-EINVAL if
countis greater than the size of the ring buffer associated with the traffic direction. See evl_create_xbuf(). -
-ENOBUFS if there is no ring buffer space associated with the outbound traffic. See evl_create_xbuf().
Attempt to write up to count bytes to the cross-buffer xbuf from
the buffer starting at buf from the out-of-band execution stage. If
not enough space is available from the cross-buffer for completing the
operation immediately, the caller blocks until enough space is freed
by reader(s) unless O_NONBLOCK is set in f_flags. The peer
application in user space can later read the output data by calling
oob_read() for the same
file referred to by the descriptor passed to evl_get_xbuf().
A cross-buffer descriptor to write to.
A buffer containing the data to be written.
The number of bytes to write starting from buf.
Operation flags. Can be either zero or O_NONBLOCK for non-blocking output.
The number of bytes written is returned on success, otherwise:
-
-EAGAIN if
O_NONBLOCKis set inf_flagsand the cross-buffer is out of memory space for receiving the requested amount of data. -
-EINVAL if
countis greater than the size of the ring buffer associated with the traffic direction. See evl_create_xbuf(). -
-ENOBUFS if there is no ring buffer space associated with the inbound traffic. See evl_create_xbuf().
